Numerous researchers and engineers have found that a group of coexisting robots work much more efficiently than several unrelated robots which can only complete one task. This theory was our basis for conception of a system of several agrobots which will work together to complete almost any given task on the farm. After getting a general idea of what we wanted to design and create, we looked to nature for inspiration. Once we brought together all our various ideas, we ultimately decided to construct our system of agrobots which had network capabilities which would allow them to communicate and share data. The agrobots will each have a specialized task in which they will assist each other in exchanging data as well as their services.
The Agrobots will need be to be competent in respect to several realms. First and foremost the robots will have to be durable, efficient, and relatively inexpensive. Farmers must get optimal performance for there money and need reliable machines. Currently, most autonomous robots are extremely expensive to repair and crafting a reliable machine is imperative. However, efficiency can be compromised in order to create an environmentally friendly robot. The bots will need to be fuel efficient and use limited natural resources.
Our robot will be a great asset to farmers everywhere. It will perform a great number of tasks to ease the job of farmers and effectively manage their time.

Multiple units will be able to communicate with each other to enhance productivity. Individual units can share information wireless via antennas they will have attached to them. Each unit will have a specific task to perform. Blue Tec diesel technology used by head automaker Mercedes Benz. This engine uses an oxidizing catalytic converter to reduce engine emissions. For more information on Blue Tec technology, visit the Mercedes site. The computers and electrical systems will be powered by lithium ion batteries. They will all have treads for traveling. They will be about 3.5 x 3.5 x 3.5 feet large.
Pesticide Bot: At optimum efficiency, the Pesticide Bot will be capable of reducing pesticide and herbicide use by 70%. The robot will drive up and down the rows in the field identifying weeds. The robot will be able to identify the weeds with the aid of the autonomous navigational software and computerized image processing which will allow the robot to differentiate between weeds and crops. The image processor will be given specific parameters to identify weeds in respect to shape, size, color, and symmetry of the leaves. Once identifying the weed type, the mechanical arm will spray the corresponding amount of pesticide or remove it from the ground. With the aid of an infrared camera and the differential GPS system, the robotís intuitive auto navigational software will be able to guide it through any terrain.
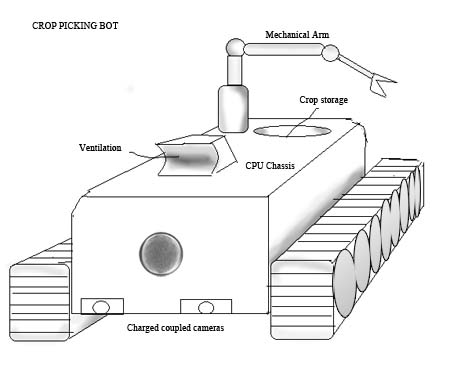
Crop Picking Bot: One of the robotís will be delegated to the sole task of picking crops when they are perfectly ripe or to the farmerís liking. With the aid of a charged coupled camera, the robot will be able to spot crops which are the perfect size and color for picking. The picking bot will be drastically more accurate than an average laborer. A mechanical arm will take commands from the CPU and pick crops which the charged coupled camera has identified. After being picked, the crops will be placed in the robotís storage area.

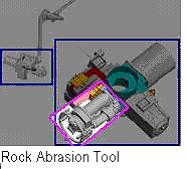
Water/Soil Bot: This robot will have the sole responsibility of measuring the quality of soil in terms of moisture and amount of minerals. The robot will take samples of soil and give them a brief analysis using a rock abrasion tool which can identify the presence of almost any rock forming mineral. If further tests are needed, the robot will take a sample to the farmer. To test moisture levels, the robot will use electrical resistance blocks. The wetter the soil, the more electricity it will produce and thus have a lower resistance and vice versa. Also, a more durable, granular matrix sensor can be used to same effect, however at a higher cost. The underbody of the robot will also have sprinklers which will water the fields as it tests soil quality.
Mower Bot: This robot will be assigned the task of automatically mowing a field as per the farmer's specified parameters. It will work along other mower bots that will ensure a field's mowing in as short a time as possible. This will easily be the cheapest and simplest of the four robots. It will navigate using simple cameras and differential GPS that will allow it to move up and down rows of the field. Additionally, it will use a depth sensor to measure how deep it should mow on the field. It will maintain a connectiong with a the other bots to ensure that the robots can effectively mow the entire field.